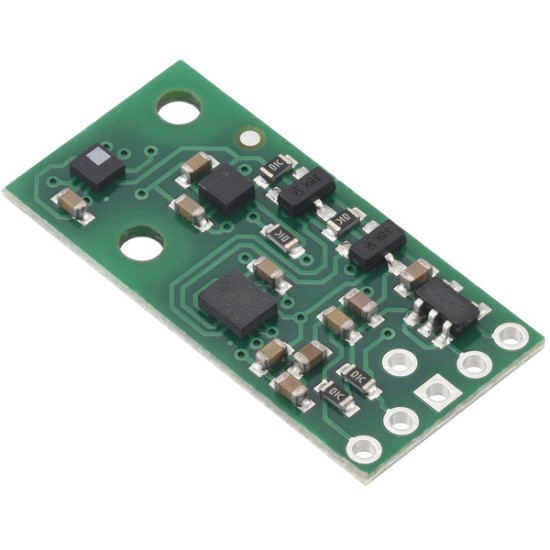
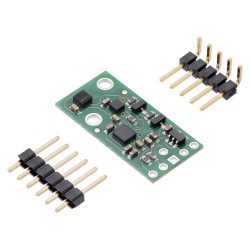
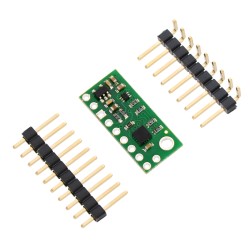
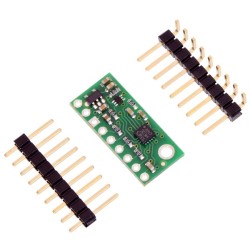
Description: The AltIMU-10 v6 is an inertial measurement unit (IMU) and altimeter that features the same LSM6DSO gyro and accelerometer and LIS3MDL magnetometer as the MinIMU-9 v6, and adds an LPS22DF digital barometer. An I²C interface accesses ten independent pressure, rotation, acceleration, and magnetic measurements that can be used to calculate the sensor’s altitude and absolute orientation. The board operates from 2.5 to 5.5 V and has a 0.1″ pin spacing.
The AltIMU-10 v6 is also pin-compatible with the MinIMU-9 v6 and offers the same functionality augmented by a digital barometer that can be used to obtain pressure and altitude measurements. It includes a second mounting hole and is only 0.2″ longer than the MinIMU-9. Any code written for the MinIMU-9 v6 should also work with the AltIMU-10 v6.
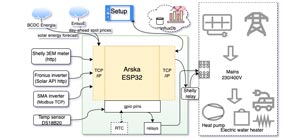
The LSM6DSO, LIS3MDL, and LPS22DF have many configurable options, including dynamically selectable sensitivities for the gyro, accelerometer, and magnetometer and selectable resolutions for the barometer. Each sensor also has a choice of output data rates. The three ICs can be accessed through a shared I²C/TWI interface, allowing the sensors to be addressed individually via a single clock line and a single data line. Additionally, a slave address configuration pin allows users to change the sensors’ I²C addresses and have two AltIMUs connected on the same I²C bus. (For additional information, see the I²C Communication section below.) The nine independent rotation, acceleration, and magnetic readings provide all the data needed to make an attitude and heading reference system (AHRS), and readings from the absolute pressure sensor can be easily converted to altitudes, giving you a total of ten independent measurements (sometimes called 10DOF). With an appropriate algorithm, a microcontroller or computer can use the data to calculate the orientation and height of the AltIMU board. The gyro can be used to very accurately track rotation on a short timescale, while the accelerometer and compass can help compensate for gyro drift over time by providing an absolute frame of reference. The respective axes of the two chips are aligned on the board to facilitate these sensor fusion calculations. (For an example of such a system using an Arduino, see the picture below and the Sample Code section at the bottom of this page.)
The carrier board includes a low-dropout linear voltage regulator that provides the 3.3 V required by the LSM6DSO, LIS3MDL, and LPS22DF, allowing the module to be powered from a single 2.5 V to 5.5 V supply. The regulator output is available on the VDD pin and can supply almost 150 mA to external devices. The breakout board also includes a circuit that shifts the I²C clock and data lines to the same logic voltage level as the supplied VIN, making it simple to interface the board with 5 V systems. The board’s 0.1″ pin spacing makes it easy to use with standard solderless breadboards and 0.1″ perfboards.
Specifications:
- Dimensions: 1.0″ × 0.5″ × 0.1″ (25 mm × 13 mm × 3 mm)
- Weight without header pins: 0.8 g (0.03 oz)
- Operating voltage: 2.5 V to 5.5 V
- Supply current: 5 mA
- Output format (I²C):
- Gyro: one 16-bit reading per axis
- Accelerometer: one 16-bit reading per axis
- Magnetometer: one 16-bit reading per axis
- Barometer: 24-bit pressure reading (4096 LSb/mbar)
- Sensitivity range:
- Gyro: ±125, ±250, ±500, ±1000, or ±2000°/s
- Accelerometer: ±2, ±4, ±8, or ±16 g
- Magnetometer: ±4, ±8, ±12, or ±16 gauss
- Barometer: 260 mbar to 1260 mbar (26 kPa to 126 kPa)
A 1×6 strip of 0.1″ header pins and a 1×5 strip of 0.1″ right-angle header pins are included, as shown in the picture below. You can solder the header strip of your choice to the board for use with custom cables or solderless breadboards or solder wires directly to the board itself for more compact installations. The board features two mounting holes that work with #2 or M2 screws (not included).
Documents & Sample Codes: Here
- Stock: 1
- Brand: Pololu
- Model: POLO/2863